Immediate Implant Placement to Replace a Fractured Central Incisor in a Young Patient and Management of Long Term Implant Infraposition
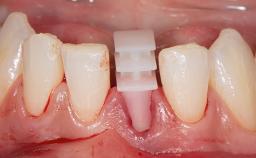
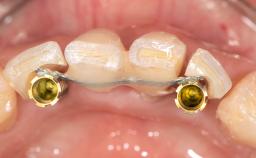
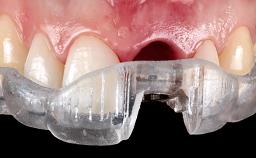
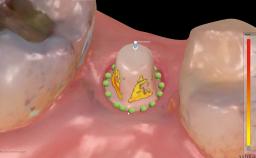
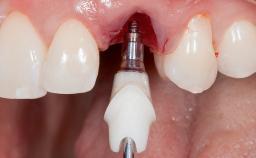
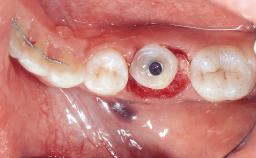
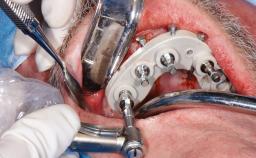
This case from Amélie Mainjot and France Lambert shows how the choice of a screw-retained restoration—which allows adjustment of the profile design over time—was key to managing complications successfully. The authors’ strategic approach avoided a crown remake while also compensating for a soft tissue mismatch. A healthy 20-year-old woman, a non-smoker, presented at the emergency department of the University Hospital of Liège in February 2011 with multiple vertical fractures of tooth 21, incisal fractures of tooth 31, and an enamel and dentin fracture of tooth 32. No tooth luxation was observed. Radiographs confirmed multiple root fractures on tooth 21, including a vertical infrabony fracture, indicating that the tooth was not restorable. A pulpectomy of tooth 21 and an indirect pulp cap on tooth 32 using resin-modified glass-ionomer cement (RMGIC) (Vitrebond; 3M, St. Paul, MN, USA) were performed. RMGC (Fuji IILC; GC, Tokyo, Japan) provisional restorations were placed on the injured teeth. The patient was sent for 3D imaging (multislice CT) the next day to determine the replacement strategy for tooth 21. Because of the vertical fractures, it was important to extract tooth 21 within a few days after the trauma to limit the risk of bacterial infection and consequent tissue loss.


General Risk Assessment
Patient-related Factors
| Oral hygiene | Fair |
|---|---|
| Compliance | Good |
Patient-medical Factors
| Medical Fitness | Healthy, able to undergo planned anesthesia and surgical procedure (ASA I) |
|---|---|
| Medications | No medications that would negatively affect the surgical procedure and outcomes. |
| Radiation Treatment | None |
| Growth Status | Incomplete |
Site-related Factors
| Periodontal Status | No history of periodontal disease, or any active periodontal disease. |
|---|---|
| Pathology near the implant site | None |
| Previous surgeries in planned implant site | No previous procedures. |
Surgical Classification
Surgical Complexity
| Timing of placement | Immediate Placement (extraction sockets) (Type I) |
|---|---|
| Simultaneous or Staged grafting procedures | Implant placement with simultaneous hard and soft tissue procedures |
Anatomy
| Bone Volume - Horizontal | Adequate |
|---|---|
| Bone Volume - Vertical | Adequate |
| Keratinized Tissue | Sufficient (>4 mm) |
| Soft Tissue Quality | No scars or inflammation |
| Proximity to vital anatomic structures | Minimal risk of involvement |
Adjacent Teeth
| Papilla | Complete |
|---|---|
| Recession | Absent |
| Interproximal attachment | At CEJ |
Extractions
| Radicular morphology | Uniradicular |
|---|---|
| Available apical bone to achieve primary stability | Sufficient height ( ≥ 4 mm) and width (> 2 mm around apex of planned implant) |
| Socket walls | Intact |
| Thickness of buccal wall | 2mm or greater |
| Anticipated residual defect after implant placement | 2 mm or less |
Prosthodontic Classification
Complicating Factors
| Biological | Screw-retained restorations with appropriate contours |
|---|---|
| Mechanical/Technical | Absence of contributing factors |
Prosthesis Factors
| Prosthetic volume | Adequate. Space available for ideal anatomy of the restoration |
|---|---|
| Inter-occlusal space | Adequate. Capable to create an anatomically & functionally correct planned restoration |
| Volume and characteristics of the edentulous ridge (fixed) | Adequate. No adjunctive therapy or prosthetic soft tissue replacement will be necessary |
Occlusal Factors
| Occlusal scheme | User-defined occlusal scheme achievable |
|---|---|
| Involvement in occlusion | Involvement |
| Occlusal parafunction | Absent |
Complexity
| Loading Protocol | Early/Conventional |
|---|---|
| Interim prosthesis | Tissue or interim implant supported |
| Implant-supported provisional restoration | Required, elevated esthetic and/or functional demands |
| Timing of placement | Immediate Placement (extraction sockets) (Type I) |
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code