Immediate Replacement of Four Mandibular Anterior Teeth with a Conventionally Loaded Implant-Supported Fixed Dental Prosthesis
This case from German Gallucci, Adam Hamilton, and Teresa Chanting Sun details immediate placement with a conventional loading protocol (type 1C). It demonstrates a digital workflow combined with risk assessment to determine the best possible treatment approach for replacing mandibular anterior teeth.
A 63-year-old female patient was referred by a periodontist for consultation and assessment with regard to implant rehabilitation of the mandibular incisors. The patient presented in good health with no history of smoking or significant medical history. The patient’s chief complaint was mobility of the mandibular anterior dentition. She had a history of periodontal disease, which had been treated and followed by a periodontist with regular maintenance every four months over the previous ten years.


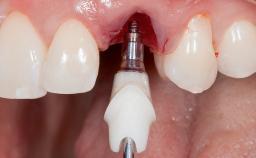
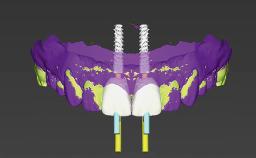
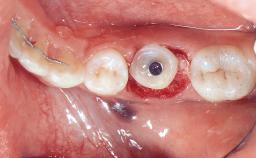
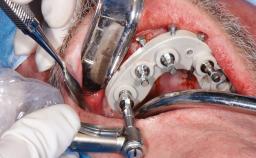
General Risk Assessment
Patient-related Factors
| Oral hygiene | Good |
|---|---|
| Compliance | Good |
Patient-medical Factors
| Medical Fitness | Healthy, able to undergo planned anesthesia and surgical procedure (ASA I) |
|---|---|
| Medications | No medications that would negatively affect the surgical procedure and outcomes. |
| Radiation Treatment | None |
| Growth Status | Complete |
Site-related Factors
| Periodontal Status | History of periodontal disease, or active periodontal disease that is controlled and stable. |
|---|---|
| Pathology near the implant site | None |
| Previous surgeries in planned implant site | No previous procedures. |
Surgical Classification
Surgical Complexity
| Timing of placement | Immediate Placement (extraction sockets) (Type I) |
|---|---|
| Simultaneous or Staged grafting procedures | Implant placement without adjunctive procedures |
| Number of implants | Two - Three |
Anatomy
| Keratinized Tissue | Sufficient (>4 mm) |
|---|---|
| Soft Tissue Quality | No scars or inflammation |
| Proximity to vital anatomic structures | Minimal risk of involvement |
Adjacent Teeth
| Papilla | Deficient |
|---|---|
| Recession | Present |
| Interproximal attachment | Below CEJ |
Extractions
| Radicular morphology | Uniradicular |
|---|---|
| Available apical bone to achieve primary stability | Sufficient height ( ≥ 4 mm) and width (> 2 mm around apex of planned implant) |
| Socket walls | Intact |
| Thickness of buccal wall | 2mm or greater |
| Anticipated residual defect after implant placement | 2 mm or less |
Prosthodontic Classification
Complicating Factors
| Biological | Screw-retained restorations with appropriate contours |
|---|---|
| Mechanical/Technical | Absence of contributing factors |
| Planned contour of tissue-fitting surfaces | Appropriate contours (hygienic - accessible for maintenance) |
Prosthesis Factors
| Prosthetic volume | Adequate. Space available for ideal anatomy of the restoration |
|---|---|
| Inter-occlusal space | Adequate. Capable to create an anatomically & functionally correct planned restoration |
| Volume and characteristics of the edentulous ridge (fixed) | Adequate. No adjunctive therapy or prosthetic soft tissue replacement will be necessary |
Occlusal Factors
| Occlusal scheme | User-defined occlusal scheme achievable |
|---|---|
| Involvement in occlusion | Involved with guidance |
| Occlusal parafunction | Absent |
Complexity
| Loading Protocol | Early/Conventional |
|---|---|
| Interim prosthesis | Tooth supported |
| Implant-supported provisional restoration | Required, elevated esthetic and/or functional demands |
| Number of implants | >2 (non-splinted) or ≥ 2 (splinted) |
| Timing of placement | Immediate Placement (extraction sockets) (Type I) |
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code