Treatment of the Atrophic Maxilla Using Two Standard Implants and Two Zygomatic Implants Immediately Loaded with a Fixed Restoration
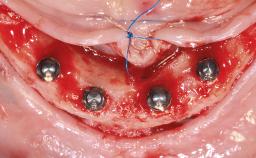
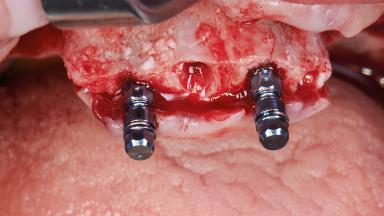
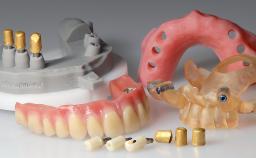
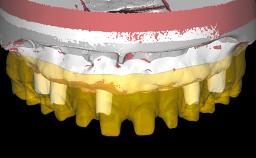
A 65-year-old woman was referred to our clinic by another dentist she had recently visited and who had diagnosed a compromised and complex clinical and anatomical situation. She complained of pain and difficulty when chewing, instability of her maxillary prosthesis, and unsatisfactory esthetics. She had received maxillary implants restored with partial fixed dental prostheses, but no stable clinical solution had been achieved. She expressed a preference for a fixed maxillary rehabilitation.

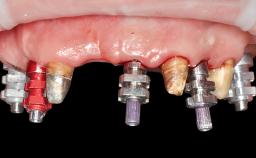

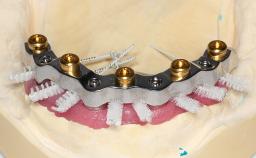
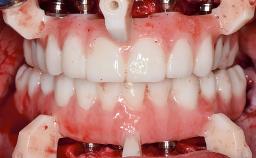
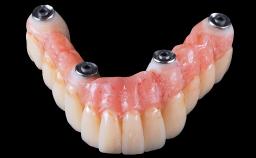
General Risk Assessment
Patient-related Factors
| Oral hygiene | Fair |
|---|---|
| Compliance | Adequate |
Patient-medical Factors
| Medical Fitness | Healthy, able to undergo planned anesthesia and surgical procedure (ASA I) |
|---|---|
| Medications | No medications that would negatively affect the surgical procedure and outcomes. |
| Radiation Treatment | None |
| Growth Status | Complete |
Site-related Factors
| Access | Adequate |
|---|---|
| Pathology near the implant site | None |
| Previous surgeries in planned implant site | Previous procedures resulting in significant bone and soft tissue changes. |
Surgical Classification
Surgical Complexity
| Timing of placement | Immediate Placement (extraction sockets) (Type I) |
|---|---|
| Simultaneous or Staged grafting procedures | Implant placement without adjunctive procedures |
| Number of implants | > Three |
Anatomy
| Keratinized Tissue | Sufficient (>4 mm) |
|---|---|
| Soft Tissue Quality | Presence of scars and inflammation |
| Proximity to vital anatomic structures | High risk of involvement |
Extractions
| Radicular morphology | Uniradicular |
|---|---|
| Available apical bone to achieve primary stability | Sufficient height ( ≥ 4 mm) and width (> 2 mm around apex of planned implant) |
| Socket walls | Intact |
| Thickness of buccal wall | 2mm or greater |
| Anticipated residual defect after implant placement | 2 mm or less |
Prosthodontic Classification
Complicating Factors
| Biological | Framework/Bar with appropriate contours and accessible maintenance procedures |
|---|---|
| Mechanical/Technical | Presence of non-critical contributing factors |
| Planned contour of tissue-fitting surfaces | Appropriate contours (hygienic - accessible for maintenance) |
Prosthesis Factors
| Prosthetic volume | Adequate. Space available for ideal anatomy of the restoration |
|---|---|
| Inter-occlusal space | Adequate. Capable to create an anatomically & functionally correct planned restoration |
| Volume and characteristics of the edentulous ridge (fixed) | Inadequate. Adjunctive therapy or prosthetic materials may be necessary to achieve optimal result |
Occlusal Factors
| Occlusal scheme | User-defined occlusal scheme achievable |
|---|---|
| Involvement in occlusion | Involvement |
| Occlusal parafunction | Absent |
Complexity
| Loading Protocol | Immediate |
|---|---|
| Implant-supported provisional restoration | Required, elevated esthetic and/or functional demands |
| Number of implants | >2 (non-splinted) or ≥ 2 (splinted) |
| Timing of placement | Immediate Placement (extraction sockets) (Type I) |
Esthetic Risk Assessment
Edentulous Esthetic Risk Assessment (fixed)
| Facial Support | Minimal changes in facial support tolerated by patient |
|---|---|
| Labial Support | Minimal changes in lip support tolerated by patient |
| Upper Lip Length | Long upper lip (>20mm) |
| Buccal Corridor | Wide Corridor |
| Smile Line | No display of the Maxillary ridge at full smile |
| Maxillomandibular Relationship | Class I |
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code