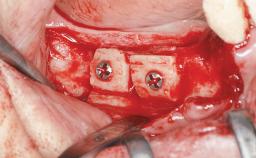
Ridge Preservation and Implant Placement for a Fixed Dental Prosthesis After a Car Accident
It is well known to clinicians that any removal of teeth will, over time, cause the dimensions of the alveolar ridge to be reduced by resorption of the bundle bone and by changes related to external modeling. This development is particularly evident in the crestal region with its thin buccal bone that consists of bundle bone almost entirely. The facial bone will rapidly resorb as blood supply from the periodontal ligament gets disrupted (Araújo and Lindhe 2005). There is no reason why traumatic tooth loss should not have the same consequences. It takes more than achieving implant osseointegration for a treatment outcome to be considered successful. No deficiency of bone or soft tissue is acceptable when an ideal esthetic outcome is the goal. Several articles (Sanz and coworkers 2011; Vignoletti and coworkers 2011) have reported on techniques of improving the alveolar ridge for implant treatment, notably focusing on protecting tissues from resorption.


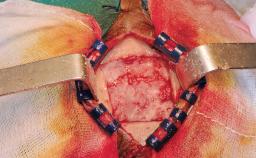
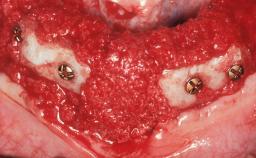
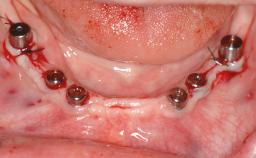
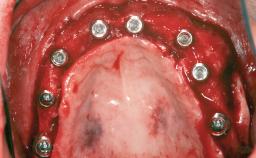
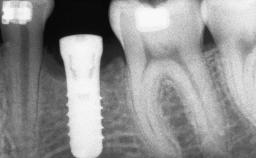
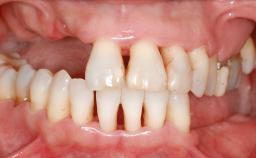
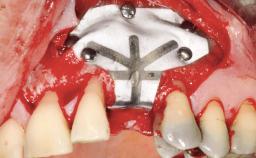
General information
| Case Type | Extended Space |
|---|---|
| Jaw | Maxilla |
| Area | Anterior|Posterior |
| # of Teeth | 6 |
| # of Implants | 4 |
| Type of Implants | One-Piece|Reduced-Diameter |
| Attachment | One-Piece|Reduced-Diameter |
| Bone Augmentation | Horizontal|Simultaneous|Sinus Floor Elevation|Staged |
|---|---|
| Augmentation Materials | Xenogenous|Membrane |
| Guided Surgery | No |
| Soft Tissue Grafting | None |
| Abutment Type | Standard |
| Prosthesis Type | FDP |
Esthetic Risk Assessment
| Esthetic Risk Factors | Low | Medium | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Status | Healthy | Compromised | |
| Smoking Habit | Non-smoker | Light smoker (< 10 cigarettes per day) | Heavy smoker (>= 10 cigarettes per day) |
| Patient's Esthetic Expectations | Low | Medium | High |
| Lip Line | No exposure of papillae | Exposure of papillae | Full exposure of mucosa margin |
| Periodontal Phenotype | Low-scalloped, thick | Medium-scalloped, medium-thick | High-scalloped, thin |
| Shape of Tooth Crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at Implant Site | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone Level at Adjacent Teeth | <= 5 mm to contact point | 5.5 to 6.5 mm to contact point | > 7 mm to contact point |
| Prosthodontic Status of Neighboring Teeth | Virgin | Restored | |
| Width of Edentulous Span | 1 tooth (>= 7 mm) | 1 tooth (< 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft Tissue Anatomy | Intact | Defective | |
| Bone Volume | Horizontally and vertically sufficient | Horizontally deficient | Deficient vertically or deficient vertically AND horizontally |
* General SAC assessment modifiers that are also part of the ERA. To avoid redundancy they are listed in this section even if no complete ERA has been made.
** Not applicable to the ERA of immediate placement cases and replaced by "Socket Integrity" listed below under "Surgical SAC Classification". For all other placement types this value is a classification determinant and listed here even if no complete ERA has been made.
Surgical SAC classification
| SAC Level | Complex |
|---|---|
| Defining Characteristics | More than three missing teeth to be replaced with an implant-borne prosthesis or prostheses |
| Modality | - |
| Placement Protocol | Early or late implant placement |
| Tooth Site | - |
| Socket Morphology | - |
| Socket Integrity | - |
| Bone Volume | Deficient vertically or deficient vertically AND horizontally |
| Anatomic Risk | High |
| Esthetic Risk | High |
| Complexity | High |
| Risk of Complications | High |
Prosthodontic SAC classification
| SAC Level | Advanced |
|---|---|
| Defining Characteristics | Up to three missing teeth to be replaced with an implant-borne restoration or restorations |
| Loading Protocol | Conventional or early |
| Retention | Cemented, with prosthesis margin < 3mm submucosal Cemented, with prosthesis margin < 3mm submucosal |
| Maxillomandibular Relationship | - |
| Mesio-Distal Space | Anatomic space corresponding to the missing teeth +/- 1 mm |
| Inter-Arch Distance | > 8 mm |
| Bruxism | Absent |
| Esthetic Risk | High |
| Provisional Implant-Supported Prosthesis | Prosthodontic margin < 3 mm apical to mucosal crest Prosthodontic margin < 3 mm apical to mucosal crest |
| Interim Prosthesis during Healing | - - |
| Occlusion/Articulation | Harmonious |
| Occlusal Scheme/Issues | - |
Surgical SAC Modifiers
| Periodontal Status | Healthy |
|---|
Prosthodontic SAC Modifiers
| Soft Tissue Contour and Volume | Slightly compromised |
|---|
General SAC Modifiers
| Oral Hygiene and Compliance | Good |
|---|---|
| Access | Adequate |
| Craniofacial/Skeletal Growth | Completed |
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code