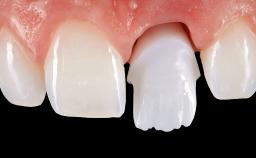
Guided Immediate Placement of a Ceramic Implant in a Maxillary Right Second Premolar and Immediate Restoration with a CAD/CAM-Fabricated Provisional Crown
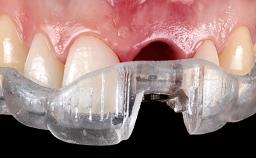
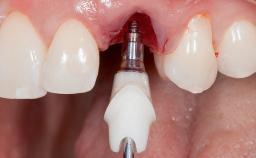
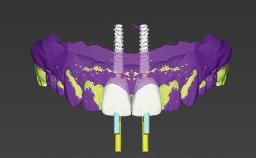
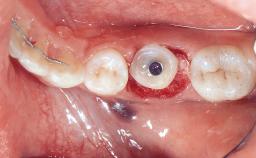
With this case, André Chen highlights the importance of the correct 3D positioning of monotype ceramic implants placed immediately in a single-tooth situation. One-piece implants have biological advantages but placing them in the correct prosthodontic position can be a challenge.
Every tooth extraction initiates a cascade of continuous events that lead to hard and soft tissue volumetric and linear changes (Araújo and coworkers 2019; Grunder 2011).
In recent years, implant dentistry has aimed to understand the biology of alveolar socket/bone remodeling in order to minimize the impact on linear and volumetric parameters, with lower morbidity and fewer esthetic problems (Atieh and coworkers 2015).
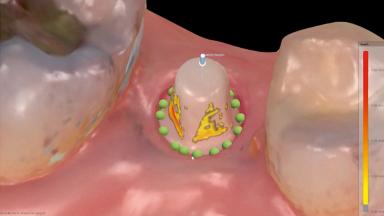

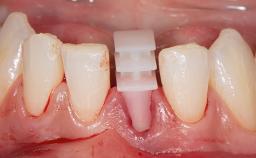
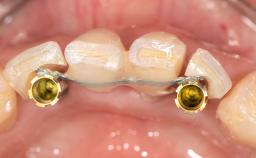
General Risk Assessment
Patient-related Factors
| Oral hygiene | Good |
|---|---|
| Compliance | Good |
Patient-medical Factors
| Medical Fitness | Healthy, able to undergo planned anesthesia and surgical procedure (ASA I) |
|---|---|
| Medications | No medications that would negatively affect the surgical procedure and outcomes. |
| Radiation Treatment | None |
| Growth Status | Complete |
Site-related Factors
| Periodontal Status | No history of periodontal disease, or any active periodontal disease. |
|---|---|
| Access | Adequate |
| Pathology near the implant site | None |
| Previous surgeries in planned implant site | No previous procedures. |
Surgical Classification
Surgical Complexity
| Timing of placement | Immediate Placement (extraction sockets) (Type I) |
|---|---|
| Simultaneous or Staged grafting procedures | Implant placement without adjunctive procedures |
Anatomy
| Keratinized Tissue | Sufficient (>4 mm) |
|---|---|
| Soft Tissue Quality | No scars or inflammation |
| Proximity to vital anatomic structures | Minimal risk of involvement |
Adjacent Teeth
| Papilla | Complete |
|---|---|
| Recession | Absent |
| Interproximal attachment | At CEJ |
Extractions
| Radicular morphology | Uniradicular |
|---|---|
| Available apical bone to achieve primary stability | Sufficient height ( ≥ 4 mm) and width (> 2 mm around apex of planned implant) |
| Socket walls | Intact |
| Thickness of buccal wall | 2mm or greater |
| Anticipated residual defect after implant placement | 2 mm or less |
Prosthodontic Classification
Complicating Factors
| Biological | Cement-retained restorations with appropriate contours |
|---|---|
| Mechanical/Technical | Absence of contributing factors |
Prosthesis Factors
| Prosthetic volume | Adequate. Space available for ideal anatomy of the restoration |
|---|---|
| Inter-occlusal space | Adequate. Capable to create an anatomically & functionally correct planned restoration |
| Volume and characteristics of the edentulous ridge (fixed) | Adequate. No adjunctive therapy or prosthetic soft tissue replacement will be necessary |
Occlusal Factors
| Occlusal scheme | User-defined occlusal scheme achievable |
|---|---|
| Involvement in occlusion | Minimal or no involvement |
| Occlusal parafunction | Absent |
Complexity
| Loading Protocol | Immediate |
|---|---|
| Implant-supported provisional restoration | Required, non-esthetic site and/or functional demands |
| Timing of placement | Immediate Placement (extraction sockets) (Type I) |
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code