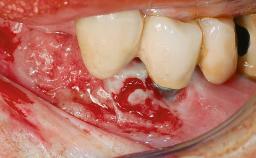
Excess Cement Resulting in Peri-implant Infection Presenting as a Draining Sinus Tract
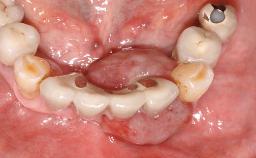
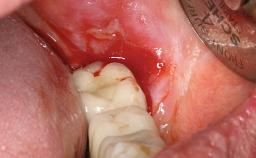
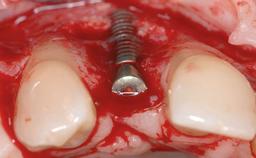
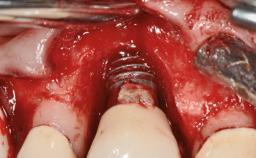
Biological complications caused by undetected cement residue have been receiving much attention. Excess cement might be responsible not only for rapidly developing of peri-implantitis, but also for delayed or chronic manifestations of the disease many years after cementation (Wilson 2009; Linkevicius and coworkers 2013). Invitro and clinical studies have shown that it is very difficult or even impossible to completely clean up excess cement at subgingival margins, so popular in cemented restorations (Agar and coworkers 1997; Linkevicius and coworkers 2011, 2012). Possible outcomes of biological complications due to excess cement range from temporary inflammation of the peri-implant soft tissues without any serious esthetic and functional consequences all the way to implant loss. This report describes a case of peri-implantitis caused by residual cement; as well as the management and quite unusual resolution of the complication. The patient presented in 2009 with a draining sinus tract, tenderness on chewing, and tissue contact above the implant-supported restoration. The implant had been restored approximately three years before.


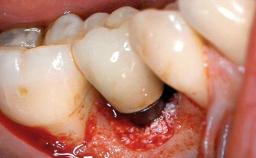
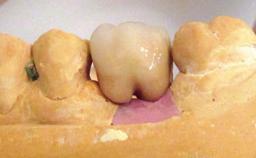
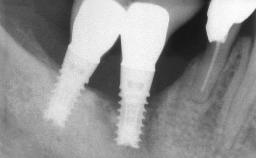

General information
| Case Type | Single-Tooth Space |
|---|---|
| Jaw | Maxilla |
| Area | Posterior |
| # of Teeth | 1 |
| # of Implants | 1 |
| Type of Implants | Two-Piece |
| Attachment | Two-Piece |
| Bone Augmentation | No |
|---|---|
| Augmentation Materials | - |
| Guided Surgery | No |
| Soft Tissue Grafting | None |
| Abutment Type | Standard |
| Prosthesis Type | FDP |
Esthetic Risk Assessment
| Esthetic Risk Factors | Low | Medium | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Status | Healthy | Compromised | |
| Smoking Habit | Non-smoker | Light smoker (< 10 cigarettes per day) | Heavy smoker (>= 10 cigarettes per day) |
| Patient's Esthetic Expectations | Low | Medium | High |
| Lip Line | No exposure of papillae | Exposure of papillae | Full exposure of mucosa margin |
| Periodontal Phenotype | Low-scalloped, thick | Medium-scalloped, medium-thick | High-scalloped, thin |
| Shape of Tooth Crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at Implant Site | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone Level at Adjacent Teeth | <= 5 mm to contact point | 5.5 to 6.5 mm to contact point | > 7 mm to contact point |
| Prosthodontic Status of Neighboring Teeth | Virgin | Restored | |
| Width of Edentulous Span | 1 tooth (>= 7 mm) | 1 tooth (< 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft Tissue Anatomy | Intact | Defective | |
| Bone Volume | Horizontally and vertically sufficient | Horizontally deficient | Deficient vertically or deficient vertically AND horizontally |
* General SAC assessment modifiers that are also part of the ERA. To avoid redundancy they are listed in this section even if no complete ERA has been made.
** Not applicable to the ERA of immediate placement cases and replaced by "Socket Integrity" listed below under "Surgical SAC Classification". For all other placement types this value is a classification determinant and listed here even if no complete ERA has been made.
Surgical SAC classification
| SAC Level | Straightforward |
|---|---|
| Defining Characteristics | One missing tooth to be replaced by an implant-borne prosthesis |
| Modality | - |
| Placement Protocol | Early or late implant placement |
| Tooth Site | - |
| Socket Morphology | - |
| Socket Integrity | - |
| Bone Volume | Horizontally and vertically sufficient |
| Anatomic Risk | Low |
| Esthetic Risk | Low |
| Complexity | Low |
| Risk of Complications | Low |
Prosthodontic SAC classification
| SAC Level | Straightforward |
|---|---|
| Defining Characteristics | One missing tooth to be replaced by an implant-borne crown |
| Loading Protocol | Conventional or early |
| Retention | Screw-retained Screw-retained |
| Maxillomandibular Relationship | - |
| Mesio-Distal Space | Anatomic space corresponding to the missing tooth +/- 1 mm |
| Inter-Arch Distance | Ideal tooth height +/- 1 mm |
| Bruxism | Absent |
| Esthetic Risk | Low |
| Provisional Implant-Supported Prosthesis | - - |
| Interim Prosthesis during Healing | - - |
| Occlusion/Articulation | - |
| Occlusal Scheme/Issues | - |
Surgical SAC Modifiers
| Periodontal Status | Healthy |
|---|
Prosthodontic SAC Modifiers
| Soft Tissue Contour and Volume | - |
|---|
General SAC Modifiers
| Oral Hygiene and Compliance | Sufficient |
|---|---|
| Access | Adequate |
| Craniofacial/Skeletal Growth | Completed |
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code