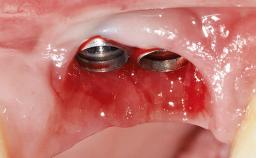
Early Implant Placement, Contour Augmentation, and Autologous Connective-Tissue Graft Using a Tunneling Technique to Replace an Upper Incisor with Generalized Gingival Recession
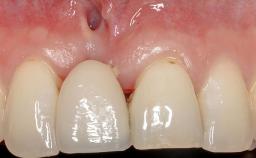
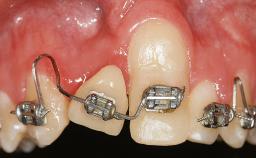
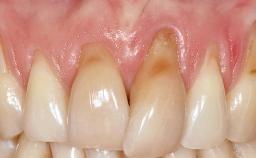
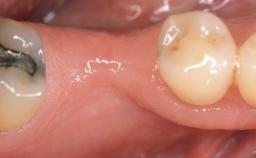
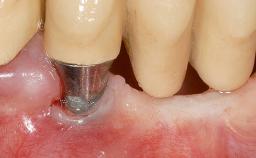
Variations in soft-tissue volume, evidenced either by an overabundance (Evian and coworkers 1993; Levine and McGuire1997; Dolt and Robbins 1997) or by a deficiency of soft or hard tissue can complicate implant-supported rehabilitations in the esthetic zone (Lorenzana 2008; Lorenzana and coworkers 2009). The present case illustrates the replacement of a failing upper left lateral incisor complicated by generalized severe gingival recession in the esthetic zone.


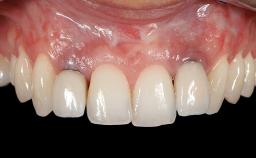
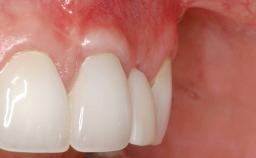
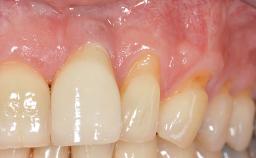
General information
| Case Type | |
|---|---|
| Jaw | Maxilla |
| Area | Anterior |
| # of Teeth | 1 |
| # of Implants | 1 |
| Type of Implants | Reduced-Diameter|Two-Piece |
| Attachment | Reduced-Diameter|Two-Piece |
| Bone Augmentation | Horizontal|Simultaneous |
|---|---|
| Augmentation Materials | Autogenous chips|Xenogenous|Membrane |
| Guided Surgery | No |
| Soft Tissue Grafting | Simultaneous |
| Abutment Type | CAD/CAM |
| Prosthesis Type | FDP |
Esthetic Risk Assessment
| Esthetic Risk Factors | Low | Medium | High |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Status | Healthy | Compromised | |
| Smoking Habit | Non-smoker | Light smoker (< 10 cigarettes per day) | Heavy smoker (>= 10 cigarettes per day) |
| Patient's Esthetic Expectations | Low | Medium | High |
| Lip Line | No exposure of papillae | Exposure of papillae | Full exposure of mucosa margin |
| Periodontal Phenotype | Low-scalloped, thick | Medium-scalloped, medium-thick | High-scalloped, thin |
| Shape of Tooth Crowns | Rectangular | Triangular | |
| Infection at Implant Site | None | Chronic | Acute |
| Bone Level at Adjacent Teeth | <= 5 mm to contact point | 5.5 to 6.5 mm to contact point | > 7 mm to contact point |
| Prosthodontic Status of Neighboring Teeth | Virgin | Restored | |
| Width of Edentulous Span | 1 tooth (>= 7 mm) | 1 tooth (< 7 mm) | 2 teeth or more |
| Soft Tissue Anatomy | Intact | Defective | |
| Bone Volume | Horizontally and vertically sufficient | Horizontally deficient | Deficient vertically or deficient vertically AND horizontally |
* General SAC assessment modifiers that are also part of the ERA. To avoid redundancy they are listed in this section even if no complete ERA has been made.
** Not applicable to the ERA of immediate placement cases and replaced by "Socket Integrity" listed below under "Surgical SAC Classification". For all other placement types this value is a classification determinant and listed here even if no complete ERA has been made.
Surgical SAC classification
| SAC Level | Complex |
|---|---|
| Defining Characteristics | One missing tooth to be replaced by an implant-borne prosthesis |
| Modality | Modality |
| Placement Protocol | Early or late implant placement |
| Tooth Site | Tooth site |
| Socket Morphology | Socket morphology |
| Socket Integrity | Socket integrity |
| Bone Volume | Deficient vertically or deficient vertically AND horizontally |
| Anatomic Risk | High |
| Esthetic Risk | High |
| Complexity | High |
| Risk of Complications | High |
Prosthodontic SAC classification
| SAC Level | Complex |
|---|---|
| Defining Characteristics | One missing tooth to be replaced by an implant-borne crown |
| Loading Protocol | Conventional or early |
| Retention | - |
| Maxillomandibular Relationship | - |
| Mesio-Distal Space | - |
| Inter-Arch Distance | - |
| Bruxism | - |
| Esthetic Risk | High |
| Provisional Implant-Supported Prosthesis | - |
| Interim Prosthesis during Healing | - |
| Occlusion/Articulation | - |
| Occlusal Scheme/Issues | - |
Surgical SAC Modifiers
| Periodontal Status | Healthy |
|---|
Prosthodontic SAC Modifiers
| Soft Tissue Contour and Volume | Significantly deficient |
|---|
General SAC Modifiers
| Oral Hygiene and Compliance | Good |
|---|---|
| Access | Adequate |
| Craniofacial/Skeletal Growth | Completed |
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code